Table of Contents
What are BID-ASK and SPREAD
Navigating the intricate landscape of market information can be quite a challenge. Many turn to the trusty tool of Googling to unearth useful insights. While seeking knowledge, one might stumble upon an objective definition by searching “spread is,” yet the results can be jarring when inquiring about “market mechanics.” A slew of initial search hits can be dominated by articles outlining broad categories like “trend, correction, reversal, level breakout, and rebound.” Imbibing such knowledge not only endangers a trader’s rationale but also their investments. To counteract this, we strive to disseminate the most unbiased market insights possible.
In our viewpoint, discussing market mechanics through terms like “reversals and breakouts” parallels discussing an internal combustion engine by merely mentioning its outward actions rather than delving into its internal processes like fuel injection, combustion, and piston movements due to gas pressure, akin to saying “the car is moving and turning left.”
The genuine mechanics of the market encompass:
- Order Matching: How orders from buyers and sellers are harmonized.
- Equilibrium Shifts: How buyers or sellers shift market balance, prompting price shifts.
- Liquidity Movement: How liquidity transfers between different assets and parties.
First, the fundamentals: Understanding the process of buying or selling an asset on an exchange:
Imagine having $10,000 and a desire to buy Bitcoin. How does an instant purchase unfold? With ease! Click the “Buy” button on the exchange terminal, and, in a fraction of time, the Bitcoin quantity your money covers will reflect in your wallet.
This seemingly routine act, something you do daily without much thought, akin to buying coffee or groceries, can be disrupted when your desired item isn’t available. You’re willing to pay extra to get that favored cup of coffee, but its absence thwarts your intent.
The same applies to purchasing Bitcoin. For your seamless buying, someone must be selling. However, they might not be as impulsive, aiming to sell above the present price. Thus, they list their offer in the order book. Coincidentally, you might also chance upon a cheaper Bitcoin deal.
BID ASK: What’s it about?
Throughout this blog, you’ll encounter fundamental concepts that are indispensable.
The market has two facets: buyers and sellers, both can engage:
- Active: Instant trading by pressing “Buy” or “Sell.”
- Passive: Pending trade where your order resides in the order book. Here comes the BID, ASK, and Spread aspects.
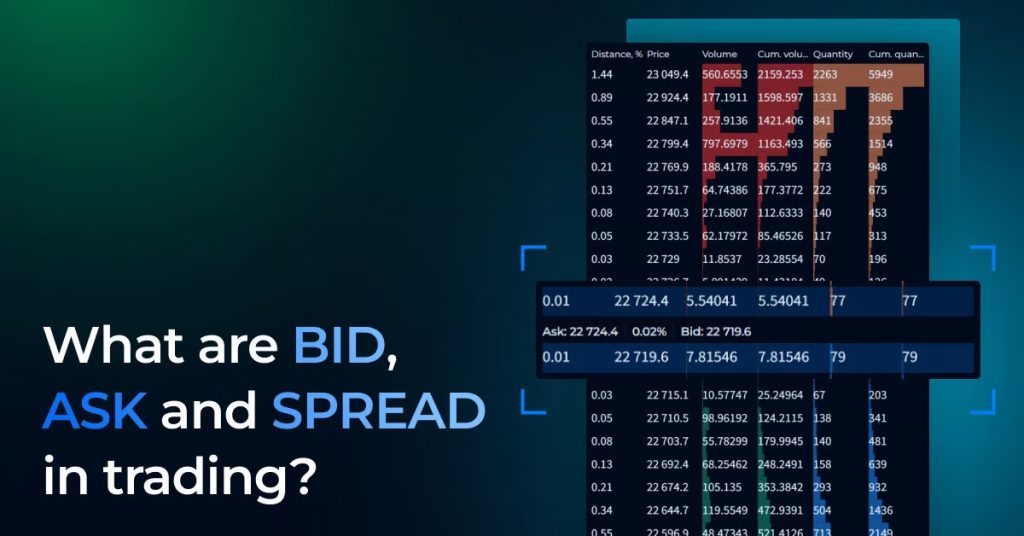
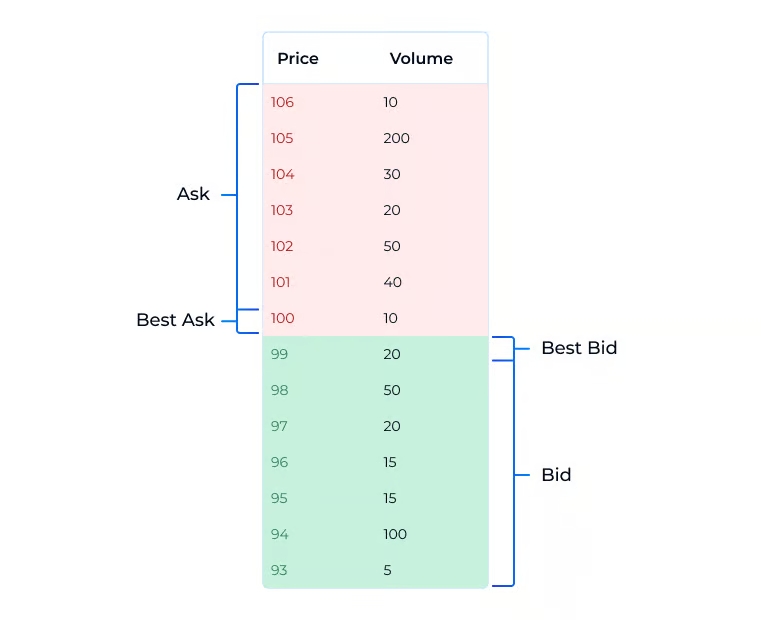
In the market, two order types exist: selling (Asks) and buying (Bids). Asks are sell orders at the order book’s top, shown in red. Bids are buy orders at the book’s bottom, marked in green.
What’s a Spread?
Understanding spreads in trading and their significance is crucial. Trading spreads is a complex topic to delve into later; for now, we’ll cover the basics.
The Spread is the difference between bid and ask prices for similar commodities in open markets.
In simpler terms, Spread is the gap between the “best” buy price (Bid) and the “best” sell price (Ask). The word “best” signifies the optimal price at that moment, though it’s practically the nearest market price.
A narrow Spread occurs when Bid and Ask prices are nearly identical, while a wider Spread arises as the gap between them widens. This divergence emerges because buyers seek lower purchase prices and higher sale prices. The Resonance platform’s Depth Density tool displays the Spread.
Conclusions
Urgently hitting “Sell” for Bitcoin prompts the exchange to match your order with the closest Bid. The reverse holds when purchasing. If time is short and you already own the asset but want to sell at a higher price, you can enter an Ask. Your sell order resides in the Ask section of the order book, awaiting a taker.
These are the fundamental, transparent, and authentic market mechanisms: buying engages sell orders, and selling involves buy orders.
These bedrock pricing principles have etched their legacy. Guided by these mechanisms, traders continue to scrutinize market dynamics, analyze, marshal evidence, and ultimately profit.
A cryptocurrency exchange is an online platform where you can buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others.
Safety varies by exchange. Look for platforms with strong security measures, like two-factor authentication and cold storage for funds.
Consider factors like security, fees, available coins, user interface, and customer support.
Centralized exchanges are managed by a company, while decentralized exchanges operate without a central authority.
Many exchanges require Know Your Customer (KYC) verification for security and regulatory compliance.
Trading fees vary but typically include maker fees (for adding liquidity) and taker fees (for removing liquidity).
Yes, most exchanges offer cryptocurrency-to-cryptocurrency trading pairs.
Withdrawal times depend on the exchange and the cryptocurrency. Some are instant, while others may take hours or even days.
A wallet address is like a bank account number for cryptocurrencies. It’s required to send your crypto to the right place.
Yes, depending on your country’s tax laws, trading cryptocurrencies may have tax consequences. Consult a tax professional for guidance.
Yes, many cryptocurrency exchanges operate 24/7, allowing you to trade at any time.
A market order buys or sells at the current market price, while a limit order sets a specific price at which you want to buy or sell.
Yes, each exchange sets its own minimum and maximum trading limits, which can vary widely.
It’s not recommended. For security, it’s better to use a cryptocurrency wallet, especially for significant holdings.
Exchanges typically have account recovery processes, including password reset options and support for forgotten usernames.
Some exchanges offer insurance, but coverage can be limited. It’s essential to check an exchange’s insurance policy.
Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and be cautious of phishing scams and suspicious emails.
Yes, but it’s recommended to learn the basics of trading and understand the risks involved before you start.
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to the value of a fiat currency like the US dollar. They provide stability and are commonly used for trading and transferring funds on exchanges.
Yes, regulations vary by country. Many countries have implemented or are considering regulations to govern cryptocurrency exchanges for consumer protection and financial stability.