What is Near Protocol?
Near Protocol, often referred to simply as NEAR, is a decentralized blockchain platform designed to enable the creation and execution of (dApps). It aims to provide a scalable and developer-friendly environment for building and deploying blockchain-based applications. Next, we will look at some of its key features and aspects.

Table of Contents
NEAR Protocol is a blockchain platform that offers a compelling array of features and capabilities, making it a versatile and developer-friendly choice for a wide range of applications. With a focus on scalability, security, and interoperability, ecosystem stands out as a robust solution for those seeking efficient transaction processing and cross-chain compatibility. In this article, we’ll delve deeper into NEAR’s unique offerings, its role in the world of decentralized applications, and the versatile NEAR token that powers its ecosystem. Whether you’re interested in DeFi, NFTs, gaming, or exploring the broader blockchain landscape, it has something to offer.
Scalability: NEAR Protocol employs a unique consensus mechanism called “Nightshade” that aims to achieve high throughput and low latency. This makes it suitable for applications that require fast and efficient processing of transactions.
Developer-Friendly: Aiming to simplify the development of decentralized applications by offering a range of developer tools, including the Software Development Kit (SDK), a Rust-based smart contract language called AssemblyScript, and a user-friendly wallet.
Interoperability: Designed to be interoperable with other blockchains and networks, allowing for the seamless movement of assets and data between different ecosystems. This interoperability is achieved through features like the Rainbow Bridge, which connects NEAR to the Ethereum blockchain.
Security: NEAR Protocol places a strong emphasis on security, with features like sharding and a unique approach to contract execution that helps prevent common vulnerabilities and attacks.
Decentralization: Layer 1 blockchain aims to distribute its network validators broadly, promoting decentralization and reducing the risk of centralization.
Community Governance: Has governance model that allows token holders to participate in decision-making and protocol upgrades.
Use Cases: Suitable for a wide range of decentralized applications, including decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), gaming, and more.
Token: The native cryptocurrency of NEAR Protocol is called NEAR, which is used for various purposes within the network, including paying for transaction fees and participating in governance.
All in all it’s one of many blockchain platforms in the rapidly evolving blockchain ecosystem, and its focus on scalability, developer-friendliness, and security makes it a notable player in the space.
The vision behind NEAR Protocol
The inception of NEAR Protocol was born from the visionary minds of Alexander Skidanov and Ilya Polosukhin. They aspired to construct a decentralized application platform that embodies scalability, security, and user-friendliness. Recognizing the transformative potential of blockchain technology in data exchange and storage, they were quick to identify the limitations of existing platforms in terms of scalability and user experience.
To tackle these challenges head-on, Skidanov and Polosukhin conceived the NEAR Protocol platform, which stands atop a sharded Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain. The ingenious sharded architecture of NEAR Protocol enhances transaction processing efficiency and facilitates seamless scalability to accommodate a substantial user base. Moreover, the implementation of PoS consensus ensures the platform’s robust security and resilience against potential threats.
NEAR Protocol’s commitment to user accessibility is further exemplified through its user-centric features. These include a user-friendly blockchain programming language named Rust and an uncomplicated, intuitive user interface (UI) designed to broaden its appeal to a wider audience.
Founders
Alexander Skidanov
Distinguished software engineer and entrepreneur, renowned for co-founding NEAR Protocol in 2017, where he currently holds the role of Chief Executive Officer (CEO). Skidanov’s pivotal responsibilities encompass the strategic direction and overarching vision of NEAR Protocol, in addition to the day-to-day management of the company.
Skidanov boasts a noteworthy career in software engineering, having occupied leadership roles at prominent technology companies such as Change.org and Microsoft. His profound expertise in distributed systems and blockchain technology has earned him recognition as a pioneering figure in the field.
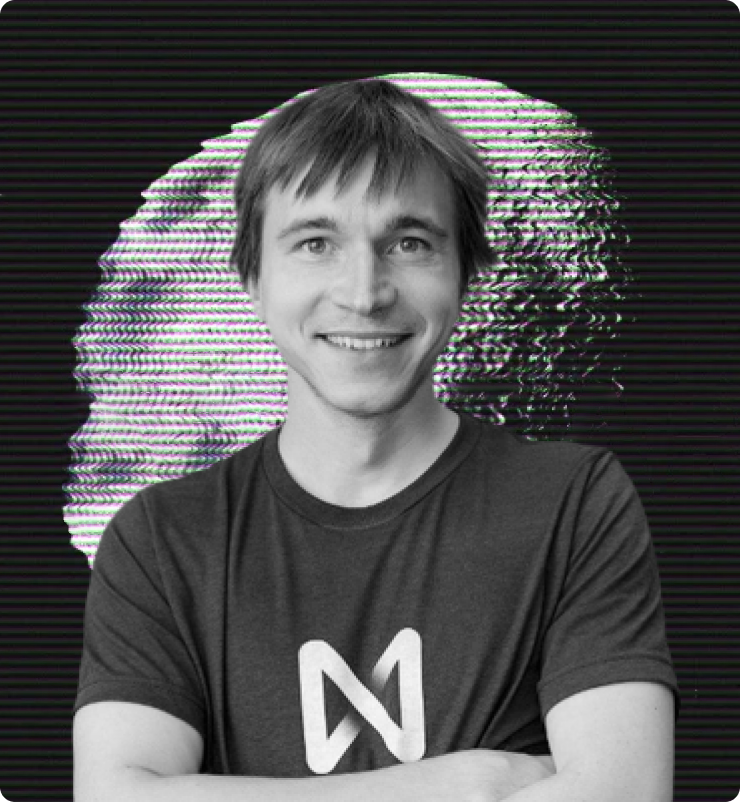
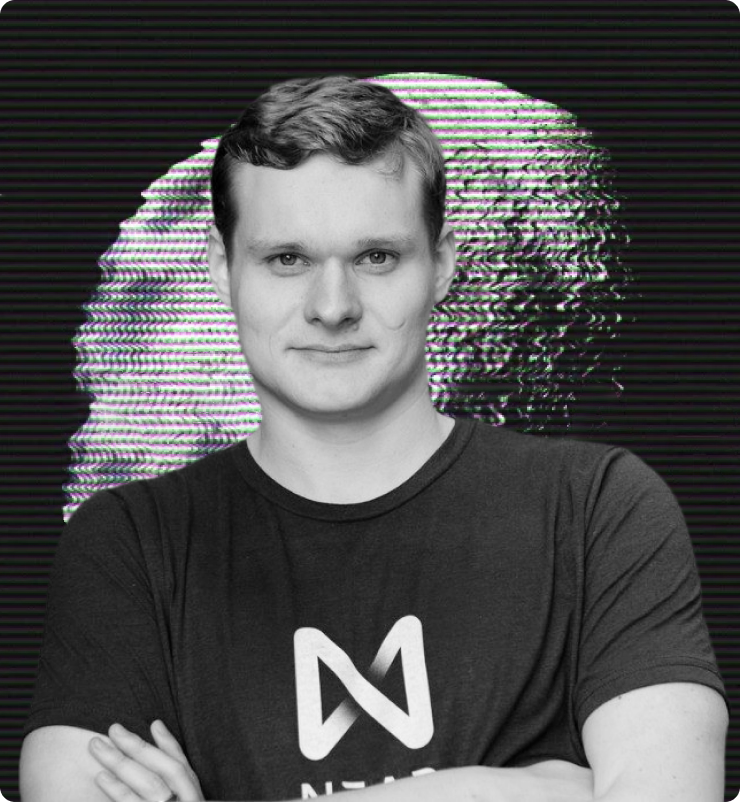


Ilya Polosukhin
another luminary in the realm of software engineering and entrepreneurship, serves as the Chief Technical Officer (CTO) of NEAR Protocol. Polosukhin shoulders the responsibility of spearheading the technical advancement of the NEAR Protocol platform and its various components.
Polosukhin brings a wealth of experience, having previously held leadership positions at esteemed technology enterprises, including Google and NVIDIA. His profound grasp of distributed systems and blockchain technology is evidenced by his prolific publication of research papers on topics such as data storage and distributed systems.
Near Protocol Nightshade Scalability
NEAR Protocol is making waves in the web3 space with its innovative approach to scalability and security. At the heart of NEAR’s groundbreaking solutions lies Nightshade, a unique sharding protocol that aims to create a “fully-sharded” network. In this article, we’ll explore the scalability challenge in blockchains and existing solutions.
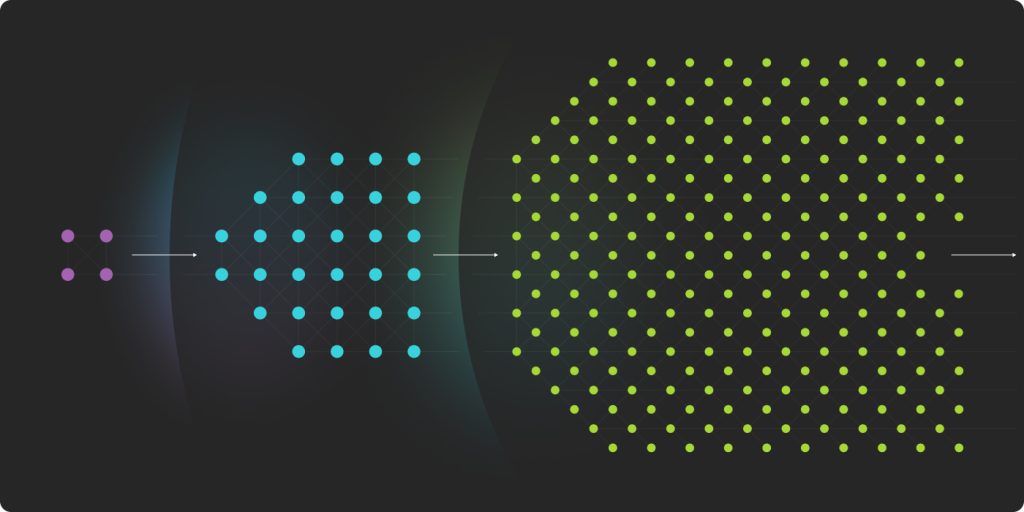
Scalability Challenge
Blockchain scalability is crucial for accommodating a growing user base while maintaining decentralization and security. Traditional blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, struggle to handle a high volume of transactions, resulting in network congestion and high fees.
Sharding as a Solution
Sharding, a horizontal scaling solution, has gained traction. It divides the network into smaller groups called “shards,” allowing nodes to store and process only a portion of the data, significantly boosting efficiency.
NEAR Nightshade Approach
Nightshade implements in phases, starting with “Simple Nightshade.” This phase shards the blockchain’s state, alleviating congestion by increasing transaction processing capacity. It’s like opening multiple checkout lines at a store.
Next, NEAR introduces “Chunk-Only Producers” to involve more community members in the consensus process. This decentralizes the network further, making it accessible to individuals with entry-level hardware.
In the final phase, “Nightshade”, fully shards both state and processing, reducing the hardware requirements for validators. This approach opens the doors to more participants and enhances network security.
Dynamic Resharding
NEAR plans to introduce “Dynamic Resharding” to adapt to changing demand, ensuring scalability and resilience to network spikes.
NEAR Smart-Contract Audits
To maintain the high security standards of the ecosystem, projects building on NEAR must undergo smart-contract audits. CertiK offers a top-notch smart-contract audit, employing AI technology and computer science experts to identify vulnerabilities.
CertiK’s audit also includes KYC verification for project teams, enhancing trust and accountability. Additionally, CertiK provides blockchain analytics tools, Bug Bounty programs, and security measures to fortify a project’s defense.
In conclusion, Nightshade is a game-changer for web3 scalability, addressing the blockchain trilemma and making blockchain technology more accessible, secure, and efficient. With the support of CertiK’s smart-contract audits and security solutions, NEAR is set to thrive in the evolving web3 ecosystem.
If you want to know more about Nightshade sharding, we recommend you to visit official paper.
Developer Friendly Blockchain
The world of blockchain technology is still in its early stages. Following the revolution brought about by Bitcoin in the financial sector, we are now entering the era of Web3, DeFi, smart contracts, and DApps. Ethereum has played a pivotal role in expanding our understanding of blockchain beyond financial transactions, becoming the first and most popular blockchain-based software platform. However, not all popular blockchain platforms are developer-friendly. In this article, we will explore the NEAR blockchain and its key components that make it one of the most developer-friendly blockchain platforms.

Affordability
Decentralization is a noble goal, but high gas costs can deter users from embracing decentralized services, leading them to opt for cheaper centralized alternatives. Ethereum-based DApps often come with hefty gas fees, causing users to hesitate. A simple smart contract on Ethereum can cost up to $7,000, while complex ones can reach $45,000. NEAR, on the other hand, is exceptionally cost-effective, with transaction costs 10,000 times lower than Ethereum. This affordability encourages users to readily engage with DApps. Interestingly, if you overpay for gas, you’ll receive a refund.
Support for Familiar Languages and Robust Tooling
In the world of smart contract development, learning various languages like Solidity, Sofia, and Clarity can be daunting. NEAR simplifies this by supporting popular languages like Rust, known for its security and versatility. Additionally, blockchain accommodates AssemblyScript, akin to TypeScript. The platform’s plan to introduce more universal languages eliminates the need for developers to learn new coding languages.
Developer-Friendly Tools
Development suite is designed to streamline developer workflows, offering a unified set of tools for building, deploying, and running applications. NEAR CLI simplifies command-line tasks, and the platform supports APIs like JavaScript and JSON RPC API.
Developer Business Models and Predictable Pricing
NEAR incentivizes smart contract creators with a built-in business model. Developers receive a 30% transaction fee for every transaction involving the smart contract they created, and this arrangement is for a lifetime. Developers can customize how they use these funds, providing predictability in terms of costs.
The Rainbow Bridge to Ethereum
Given Ethereum’s popularity and active developer community, choosing between this two can be challenging. However, NEAR offers a solution through interoperability. The Rainbow Bridge facilitates the seamless transfer of ETH assets to NEAR, bridging the gap between the two platforms.
Learning Pathway
In collaboration with Figment, NEAR has introduced a learning pathway for developers. This initiative allows anyone to easily learn and earn rewards for creating tutorials and gaining expertise.
Conclusion
While it is still a young blockchain, it has already established a robust ecosystem that caters to developers. This makes it easy to onboard new developers and provides existing developers with the tools to create sustainable businesses. The ecosystem continues to evolve, promising even more exciting developments in the future.

Security Measures: Strengths and Vulnerabilities
Exploring NEAR’s Security Measures
Near operates as a decentralized network, relying on collaboration among various individuals known as validators to ensure the chain’s security. The linchpin of this collaboration is the consensus mechanism, a trustless agreement method used by validators to establish the accurate shared state of the digital ledger. This safeguards against devastating threats like the dreaded 51% attack.
As previously mentioned, NEAR employs a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, specifically employing a unique variant called Thresholded Proof of Stake (TPoS).
TPoS functions in a manner quite akin to traditional PoS. Validators commit (lock up) their NEAR tokens to gain the privilege of processing transactions, validating new blocks, and supervising other validators. These tokens can either originate from the validator’s own holdings or be delegated to them by other users. In return for these pivotal tasks, validators are compensated with a predetermined amount of tokens every epoch, approximately every 12 hours. This reward scheme is currently set at a rate that results in validators receiving 4.5% of NEAR’s total supply annually.
TPoS introduces an election process for selecting validators, akin to an auction where the highest bidders are rewarded most generously. This TPoS system provides three primary advantages over the conventional PoS model:
No Pooling: TPoS discourages the need for stakeholders to pool their assets or computational resources, as rewards directly correlate with the staked amount. This boosts the network’s decentralization and security, eliminating the typical practice of account consolidation seen in PoS blockchains like Ethereum.
Reduced Forking: Forks are less likely to occur, as they depend on a severe network split with fewer than one-third of adversaries present. This feature maintains low transaction finality times and enhances the chain’s security.
Enhanced Security: TPoS presents a formidable challenge to potential attackers, as they would need to acquire private keys from those who collectively hold more than two-thirds of the total staked amount over the past two days—a nearly insurmountable task in practice.
Challenges in NEAR’s Security Landscape
Security framework is generally robust. It leverages the Rust programming language, known for its safety features, to mitigate coding errors that could lead to hacks and exploits. NEAR has undergone thorough audits and even introduced its own smart contract audit program for applications within its ecosystem. The Rainbow Bridge, connecting NEAR to Ethereum, is recognized for its resilience, successfully thwarting multiple attacks and offering an Immunefi bug bounty program that detects critical vulnerabilities. Furthermore, the TPoS consensus mechanism is a notable asset.
Final Remarks On NEAR’s Security
The primary concern centers around decentralization. At the time of writing, NEAR has approximately 216 validators, with the top 10 controlling 35% of the total stake and the top 17 controlling 51%. This concentration of stake among a small number of validators poses a vulnerability. Recent events, such as the Tornado Cash sanctions, serve as a stark reminder that censorship attacks from powerful entities can occur unexpectedly. Due to its stake centralization, may not be as well-prepared to withstand such an assault as it should ideally be.
What are the Use Cases for the NEAR Token?
The NEAR token serves as the native cryptocurrency of the NEAR Protocol, a decentralized platform designed for creating decentralized applications (dApps) and services

Transaction Fees
Tokens are employed to cover transaction fees within the network. Whenever users engage with a dApp or service on the NEAR network, they submit a nominal amount of tokens as a transaction fee.
Staking
Tokens are applicable for staking, a process that entails locking up a specific quantity of tokens to bolster network security and consensus. Stakers are rewarded with additional tokens for their contributions.
Governance
NEAR token holders can utilize their tokens to engage in the governance of the NEAR network. This includes participating in voting on proposals, selecting validators, and suggesting modifications to the protocol.
Rewards
NEAR compensates with tokens developers and contributors for their efforts in developing and maintaining dApps and services within the NEAR network.
Near Token
Serves several purposes within the ecosystem:
Gas Fees: Tokens are used to pay for transaction fees and computational services on the network, similar to how Ethereum uses Ether (ETH) for gas fees.
Staking: Holders can stake their tokens to secure the network and participate in block production and validation. Stakers are rewarded with additional tokens for their contributions.
Governance: Holders can participate in the governance by voting on proposals and protocol upgrades.
Access to dApps: Many decentralized applications built on the Near Protocol require tokens for various functions, such as access to premium features or in-app purchases.
Supply: The initial supply of tokens was created at the launch of the Near Protocol, and additional tokens are minted through a process called “token inflation” to reward validators and stakers for securing the network. The exact inflation rate and total supply can vary based on network parameters and governance decisions.
Technology: NEAR tokens are the digital currency used on the Near Protocol blockchain. This blockchain uses a special technology called “Nightshade” to make transactions faster and handle a lot of them at once. Tokens are used to pay for things on the network, like transaction fees and to help secure the network by “staking” them. People can also vote on changes to the network if they have NEAR tokens.
Ecosystem: Ecosystem includes various decentralized applications, wallets, and tools that support NEAR tokens. Some popular dApps and projects – Paras, Aurora, and Sweat.
Partnerships and Development: Near Protocol has attracted attention and partnerships from various blockchain and tech companies such as Google. It has also received support from venture capital firms and developers interested in building on the platform.
Wallets: To store and manage NEAR tokens, users can use wallets that are compatible with ecosystem, such as the official wallet (mynearwallet.com) and other third-party wallets.
Exchanges: Tokens can be traded on various cryptocurrency exchanges, making them accessible to users who want to buy, sell, or trade them.
Buy Near
Purchasing cryptocurrency involves considering various factors, including your location and the underlying protocol. Thankfully, acquiring NEAR Token is a straightforward and secure process through either the Binance or BybIt exchange. It offers a convenient and swift solution:

























The end is near