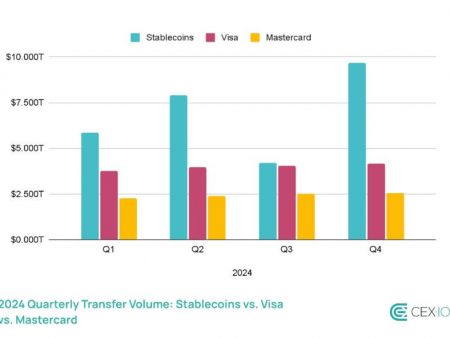
Hashdex ETF 2023
This is reported on Twitter by Bloomberg analyst James Seyffart.
Hashdex is a global pioneer in the management of cryptocurrency assets. The company collaborates with Nasdaq to develop the Nasdaq Cryptocurrency Index (NCI) and the Nasdaq Europe Cryptocurrency Index (NCIE).
The company has assets under management in the amount of $ 430 million (as of July 26, 2023)
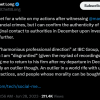
UPDATE: @hashdex has filed for a Spot #Ethereum ETF. Joining @ARKInvest /@21Shares and @vaneck_us. https://t.co/fggp7rWUvF pic.twitter.com/ZLLxuhGTtc
— James Seyffart (@JSeyff) September 12, 2023
What is Hashdex
Hashdex is a financial technology (FinTech) company that specializes in cryptocurrency and blockchain-based investment products. It was founded in Brazil in 2018 and has gained prominence for its efforts in creating cryptocurrency index funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) designed to make it easier for traditional investors to gain exposure to the cryptocurrency market.
Here are some key aspects of Hashdex:
Cryptocurrency Index Funds: Hashdex offers index funds that track the performance of a specific basket of cryptocurrencies. These funds are designed to provide investors with diversified exposure to the cryptocurrency market. For example, Hashdex has created the “HASH11” ETF on the B3 stock exchange in Brazil, which tracks a basket of cryptocurrencies.
Regulated and Compliant: Hashdex aims to provide a regulated and compliant investment avenue for cryptocurrencies. This can be appealing to institutional investors and retail investors who prefer to invest through established financial markets.
Institutional and Retail Investment: Hashdex caters to both institutional and retail investors, allowing a wide range of investors to access its cryptocurrency investment products.
Partnerships: The company has formed partnerships with traditional financial institutions and exchanges to bring its cryptocurrency investment products to a broader audience.
Educational Efforts: Hashdex has also been involved in educational initiatives to help people understand cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology better. They aim to bridge the gap between the traditional financial world and the emerging world of cryptocurrencies.
An Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund and exchange-traded product, with shares that are tradeable on a stock exchange. It combines features of both stocks and mutual funds, offering investors diversified exposure to various assets like stocks, bonds, commodities, or a mix of these.
ETFs work by pooling money from multiple investors to buy a basket of underlying assets, such as stocks or bonds. These assets are then divided into shares, which can be bought and sold on stock exchanges like individual stocks. The ETF’s market price is typically close to the net asset value (NAV) of its underlying assets.
- Diversification: ETFs offer instant diversification by holding a variety of assets within a single fund.
- Liquidity: They can be bought and sold throughout the trading day at market prices.
- Lower Costs: ETFs often have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds.
- Transparency: ETFs disclose their holdings daily, allowing investors to see what’s in the fund.
- Tax Efficiency: They tend to generate fewer capital gains due to their unique structure.
Yes, there are various types of ETFs, including:
- Equity ETFs: Track stock market indices or sectors.
- Bond ETFs: Invest in bonds, providing fixed income exposure.
- Commodity ETFs: Invest in commodities like gold, oil, or agricultural products.
- Sector ETFs: Focus on specific industry sectors, like technology or healthcare.
- Smart Beta ETFs: Follow rules-based strategies for enhanced returns.
- Inverse and Leveraged ETFs: Seek to profit from the inverse or magnified performance of an index.
- Global ETFs: Provide exposure to international markets or regions.
You can buy and sell ETFs through a brokerage account, just like individual stocks. Simply place an order to buy or sell the desired number of shares. ETF prices fluctuate throughout the trading day, so you can trade them when the market is open.
There are two primary costs associated with ETFs:
- Expense Ratio: This is the annual fee expressed as a percentage of the fund’s assets. It covers management and operational expenses. ETFs generally have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds.
- Brokerage Commissions: You may incur trading commissions when buying or selling ETFs through a brokerage account. Some brokerages offer commission-free ETF trading.
Yes, ETFs can be suitable for long-term investors. They offer diversification, liquidity, and can be used as core holdings in a portfolio. Long-term investors often use ETFs for passive, low-cost investing in various asset classes.
Yes, ETFs are popular for short-term trading due to their liquidity and ability to track specific market sectors or trends. Traders often use ETFs to implement short-term strategies, such as day trading or swing trading.
The risk associated with ETFs varies depending on the underlying assets. Equity ETFs can be subject to stock market volatility, while bond ETFs may face interest rate risk. It’s essential to research the specific ETF and its underlying assets to understand the associated risks.
Yes, many ETFs pay dividends. Equity ETFs often distribute dividends received from the underlying stocks to shareholders. Bond ETFs may also pay periodic interest payments. The frequency and amount of dividends can vary between ETFs.
ETFs are typically tax-efficient investment vehicles. They may generate fewer capital gains due to in-kind creation and redemption processes. Capital gains taxes are incurred when you sell your ETF shares at a profit. Dividends and interest income from ETFs are also subject to taxation at varying rates.
Yes, you can typically invest in ETFs through retirement accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s. Many brokerage firms offer access to ETFs within these tax-advantaged accounts, allowing you to benefit from their advantages while saving for retirement.
Information about specific ETFs can be found on financial news websites, the official websites of ETF providers (such as BlackRock or Vanguard), and brokerage platforms. These sources provide details on an ETF’s holdings, performance, expense ratio, and other relevant information.
While you can’t create your own ETF, you can build a diversified portfolio by selecting and investing in multiple ETFs that align with your investment goals and risk tolerance. This approach is often referred to as “ETF portfolio construction.”
ETFs can be traded like stocks, but some may have specific trading restrictions. For example, leveraged and inverse ETFs are designed for short-term trading and may not be suitable for long-term investors. Always review an ETF’s prospectus to understand any limitations or risks associated with trading.